Is Chinese in Asia? Understanding the Geographic and Cultural Context
China, a country in East Asia, is home to the Chinese language and one of the world’s oldest civilizations. With over 1.4 billion people, it holds a significant position on the global map, both culturally and economically. But is the Chinese language strictly confined to Asia? And how does it shape the identity of its speakers across different regions?
Geographical Location of China in Asia
China is undoubtedly located in East Asia, bordered by several countries like India, Russia, Mongolia, and Vietnam. It is the third-largest country by area in the world and dominates the eastern side of Asia.
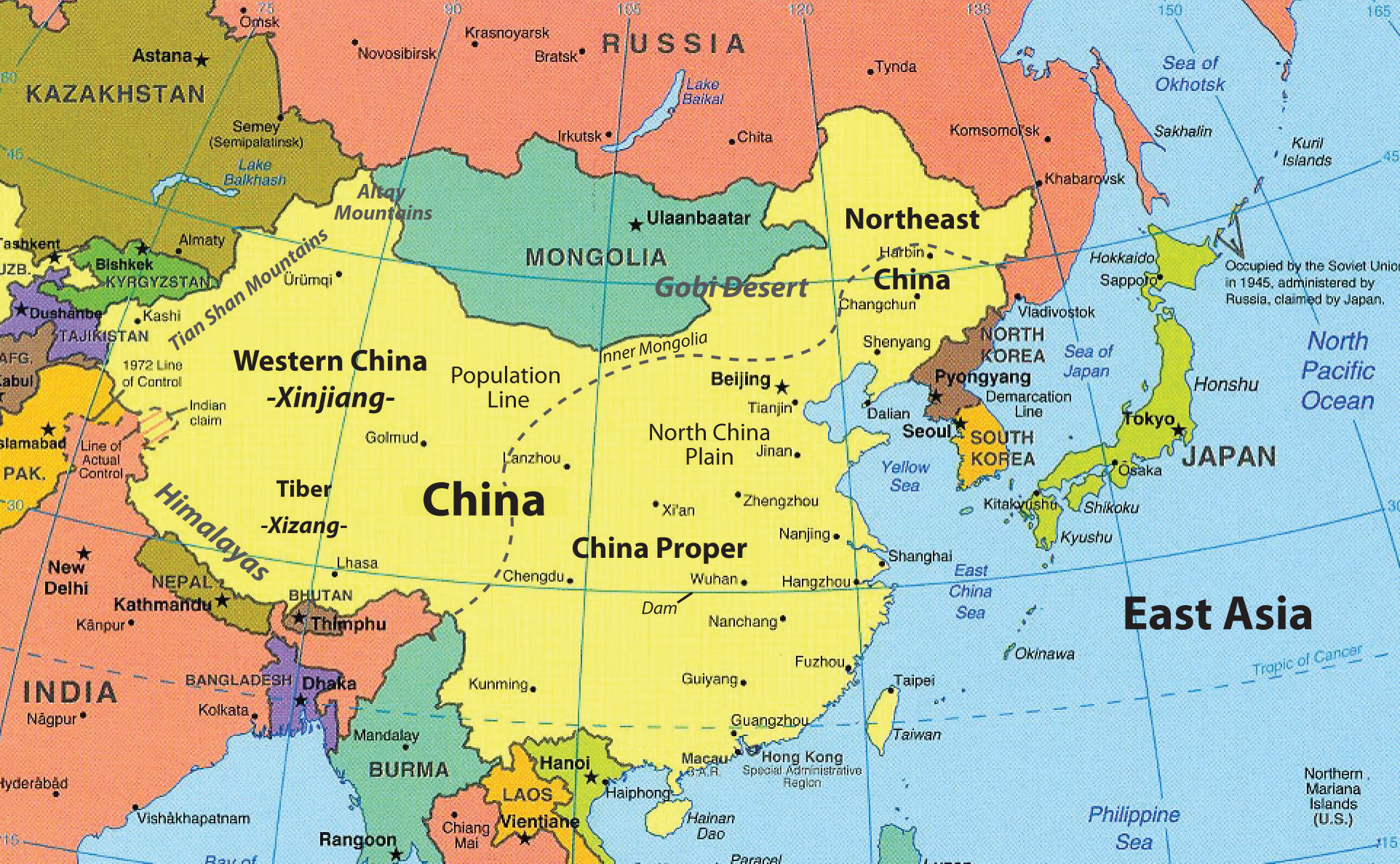
The country is divided into several regions, each with its own distinct culture and dialect. The capital city, Beijing, is the political heart of China, while Shanghai serves as its economic hub. The Great Wall of China is a prominent historical landmark, symbolizing China’s vast expanse and rich heritage.
The Chinese Language: Is It Limited to China?
Chinese is not just the language of the Chinese people. While it is primarily spoken in China, the language transcends national borders. Mandarin Chinese is the most widely spoken language in the world, with over a billion native speakers.
But does speaking Chinese mean you’re in Asia? Technically, no. Chinese communities are spread globally, and many countries have large populations of Chinese speakers, especially in regions such as Southeast Asia, North America, and Europe.
A Diverse Linguistic Landscape
The Chinese language isn’t just Mandarin. It includes a variety of other languages and dialects, such as Cantonese, Shanghainese, and Hokkien, to name a few. These dialects can vary significantly across regions, leading to unique local cultures and communities within the greater Chinese-speaking population.
For example, the Cantonese-speaking community is predominantly found in Hong Kong, Macau, and parts of Southern China. On the other hand, Mandarin, the official language of China, is widely spoken across the country and serves as a unifying linguistic force.
China’s Role in Asia’s Political and Economic Landscape
China plays a central role in Asia’s political and economic landscape. With its rapidly growing economy, China is considered one of the largest and most influential nations in the world.
Economic Powerhouse
China’s economic influence extends far beyond Asia. As a manufacturing giant, it supplies goods to countries around the world. China is also a leading player in the global supply chain, heavily involved in trade partnerships with countries across the globe, including Europe, North America, and Africa.

The Belt and Road Initiative, a global development strategy launched by China, exemplifies its growing political and economic influence beyond Asia. This initiative connects China with Europe, Africa, and other parts of the world through infrastructural investments.
Political Influence in Asia
China’s political influence is also prominent within Asia. It is a key player in regional organizations like the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), which promotes political, economic, and security-related cooperation among member states.
In addition, China’s territorial disputes with neighboring countries such as India, Japan, and countries in the South China Sea make its role in Asian politics even more significant. China’s political maneuvers often shape the dynamics of the entire continent.
The Chinese Diaspora Around the World
While China is the birthplace of the Chinese language and culture, Chinese communities are widespread across the globe. From San Francisco to Singapore, the Chinese diaspora has a rich history of migration, influencing global trade, culture, and politics.
Southeast Asia: A Strong Chinese Presence
In Southeast Asia, countries like Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand have large populations of ethnic Chinese. These regions have been home to Chinese communities for centuries. In Singapore, for example, Mandarin Chinese is one of the official languages, and the influence of Chinese culture is strong in the country’s customs, cuisine, and festivals.
China’s influence in Southeast Asia has also increased through trade and investment projects in infrastructure. With the establishment of economic partnerships, many countries in the region now rely on China as a key trading partner.
Chinese Communities in North America and Europe
In North America, especially in cities like New York and Los Angeles, Chinese communities are a prominent part of the multicultural fabric. The Chinese Exclusion Act in the 19th century limited Chinese immigration to the U.S., but today, Chinese Americans contribute significantly to the nation’s economy and culture.
In Europe, countries like the United Kingdom, France, and Germany have also seen an increase in Chinese-speaking populations due to immigration and student exchange programs. This global presence has led to the rise of Chinese businesses and cultural exchanges.
Understanding the Chinese Identity: Is It Only Tied to Geography?
Being Chinese is about more than just geography; it is a cultural and ethnic identity that transcends borders. The Chinese identity is tied to a shared history, culture, language, and set of values. While it is most strongly associated with China, the influence of Chinese culture extends far beyond the country’s borders.
Chinese Culture Around the World
Chinese traditions, such as the Chinese New Year and Dragon Boat Festival, are celebrated by millions worldwide. In cities like Vancouver, Sydney, and London, Chinese cultural festivals attract people from all backgrounds, showcasing the diversity and richness of the culture.
Moreover, Chinese food has become an international favorite. Whether it’s dim sum in Hong Kong or Kung Pao chicken in the United States, Chinese cuisine is enjoyed globally and serves as a bridge between cultures.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in Modern China
China is also known for its rapid advancements in technology and innovation. Companies like Alibaba, Tencent, and Huawei have become major players in the global tech industry.
The Chinese government has made significant investments in emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), 5G networks, and space exploration, ensuring China remains at the forefront of technological development.

In addition to this, China has expanded its internet connectivity and digital infrastructure, making it one of the most technologically advanced nations on Earth.
Conclusion: Is Chinese in Asia?
In conclusion, the Chinese language is most strongly associated with Asia, particularly China. However, its influence extends far beyond the continent, as Chinese-speaking communities thrive worldwide. Whether through trade, cultural exchange, or global migration, the Chinese language and culture play an integral role in shaping global society.
China’s political, economic, and cultural power within Asia and globally cannot be understated. From its historical presence in East Asia to its modern-day global influence, China remains a pivotal force in shaping the future of the world.
FAQs
What countries speak Chinese?
While Mandarin Chinese is primarily spoken in China, it is also spoken in countries like Taiwan, Singapore, and Malaysia. There are also significant Chinese-speaking communities in places like the United States, Canada, and Thailand.
Is Chinese a part of Asian culture?
Yes, Chinese culture is a cornerstone of Asian culture, with its long history, traditions, and influence on the continent. Chinese philosophy, art, and cuisine are integral parts of the broader Asian cultural landscape.
How many types of Chinese are there?
There are several major Chinese dialects including Mandarin, Cantonese, Shanghainese, and Hokkien. While Mandarin is the most widely spoken, each dialect has its own unique characteristics and regional significance.
Is Mandarin spoken outside of China?
Yes, Mandarin is spoken in many countries, especially in regions with Chinese diaspora communities, including Taiwan, Singapore, and parts of Southeast Asia.

Comment (0)