How Asians See the World: A Unique Perspective
The way people from different parts of the world view global issues and events can vary greatly, and Asia, with its vast diversity of cultures, traditions, and histories, offers a particularly unique perspective. Understanding how Asians see the world involves diving into a variety of perspectives shaped by history, politics, culture, and economic factors.
In this article, we’ll explore the viewpoints of various Asian regions on key global issues, the impact of modern geopolitics, and how cultural influences shape perceptions of the world. We’ll also include insightful statistics, real-world examples, and reflect on the significance of these diverse views in today’s interconnected world.
1. Cultural Diversity Across Asia
Asia is home to an incredible variety of cultures, languages, and traditions. From the bustling cities of East Asia to the tranquil landscapes of Southeast Asia, the cultural fabric of the continent is as rich as it is diverse. In countries like Japan, China, India, and Indonesia, local customs and historical narratives significantly shape how citizens view the world.
For instance, in China, Confucian values of harmony and respect for authority are deeply ingrained, influencing how people perceive global relations. In contrast, Indian society, influenced by both ancient traditions and colonial history, often takes a more open and philosophical approach to international affairs.
Regional Influences
Each region of Asia contributes to the overall worldview. Here’s a breakdown of how different areas shape perspectives:
-
East Asia (China, Japan, Korea): These countries have a deep-rooted sense of historical pride, which influences their perspectives on global power dynamics and their own place in the world. For example, Japan’s rapid modernization and recovery after World War II have shaped a pragmatic yet cautious worldview.
-
Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Thailand, Philippines): This region’s experiences with colonialism, trade, and modern conflicts create a unique blend of international outlooks. Many Southeast Asians emphasize multilateral diplomacy and cooperation in addressing global challenges.
-
South Asia (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh): The shared history of colonialism and ongoing geopolitical tensions shape the region’s complex view of the world. India’s focus on self-reliance and non-alignment in international relations offers a distinctive approach to global politics.
2. The Impact of Geopolitics
Geopolitical influences are perhaps the most immediate and visible factors shaping how Asians view the world. Countries in Asia often find themselves at the intersection of global powers, making their perspectives particularly important in international relations.
China’s Expanding Influence
In recent years, China has become a dominant force on the world stage, influencing global trade, economics, and even cultural exchanges. With its Belt and Road Initiative and increasing military presence, China’s worldview is often shaped by a desire for increased global influence.
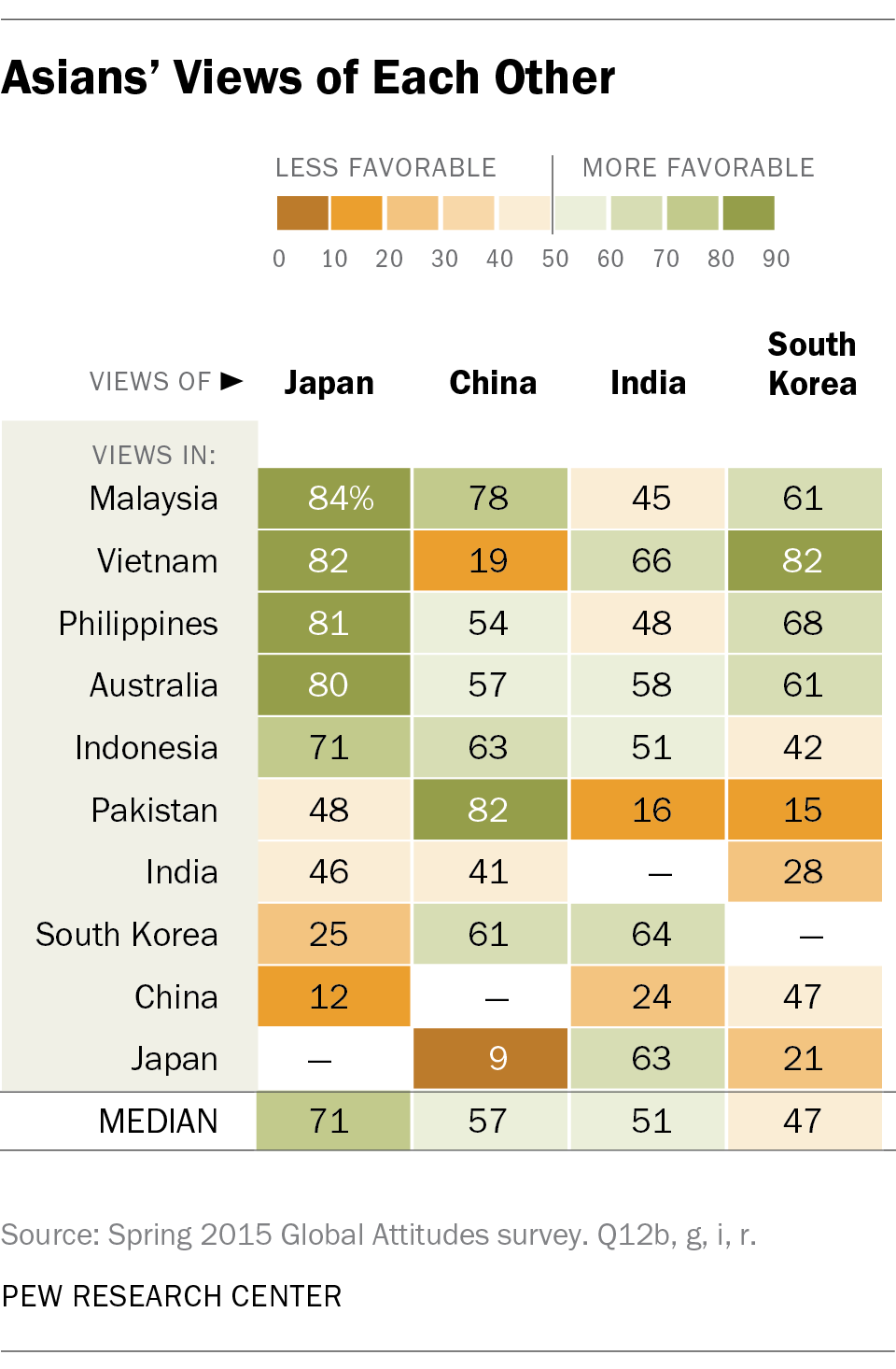
Many Asians, particularly in East and Southeast Asia, have a complex view of China’s rise. While some embrace the economic opportunities it presents, others view China’s assertiveness—particularly in the South China Sea—as a source of regional tension.
India’s Global Role
India, on the other hand, positions itself as a counterbalance to China’s growing influence, leveraging its democratic values, strategic alliances, and economic potential. India’s foreign policy is also shaped by historical ties to the West and its relationships with other Asian nations. The rise of India as a global economic player is seen as a force for global stability and a counterweight to China’s influence.

3. Global Issues and Asia’s Perspective
When it comes to global issues such as climate change, trade, and security, Asian perspectives are often different from those in the West. Asia’s rapid industrialization and urbanization, combined with its diverse ecosystems and population densities, make it particularly vulnerable to global challenges.
Climate Change
Countries in Asia are at the forefront of the climate change debate. The region is home to some of the most vulnerable nations to rising sea levels, natural disasters, and environmental degradation. Small island nations like the Maldives and Sri Lanka are already grappling with the impacts of climate change, while larger countries like China and India are struggling with pollution and resource scarcity.
Trade and Economic Growth
Asia’s economic policies reflect a unique blend of globalization and protectionism. While many Asian countries benefit from global trade, they also balance this with national interests. Trade agreements such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) highlight the region’s increasing economic integration while still ensuring economic sovereignty.
4. How Asian Media Shapes the Worldview
Media in Asia plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion and perceptions of global events. The way news is framed, what is prioritized, and how international relations are reported can all influence how people in Asia view the world.
The Role of State-Controlled Media
In countries like China, state-controlled media has a significant impact on shaping public perceptions of the outside world. The Chinese government often uses media to promote a narrative of rising power and to project strength in global matters.
In contrast, countries like India have a more diverse media landscape, where multiple outlets offer varying perspectives, allowing for a broader range of opinions on international issues. This diversity fosters a more nuanced approach to how the country interacts with the world.
5. How Asians See Western Influence
Western culture, particularly from the U.S. and Europe, has a profound influence on many parts of Asia. However, the relationship is complex. While many Asian countries have embraced Western technology, pop culture, and business practices, there are also tensions around cultural imperialism and the impact of globalization on local traditions.
In places like South Korea and Japan, Western pop culture has been embraced in the form of music, movies, and fashion. However, there’s a growing sentiment in countries like China and India that Western values may not always align with traditional Asian values, especially regarding individualism versus collectivism.
FAQs: How Do Asians See the World?
Q: How does Asia view the United States?
Many Asians have a complicated view of the United States, influenced by historical interactions, economic ties, and global politics. In some countries, the U.S. is seen as a source of innovation and democratic ideals, while in others, especially in China, it is viewed as a geopolitical rival.
Q: Are Asians united in their global views?
No, Asia is incredibly diverse, and views on global issues vary greatly across the continent. Countries in East Asia, Southeast Asia, and South Asia may share common historical experiences, but their geopolitical priorities and economic strategies often differ.
Q: How does Asia view climate change?
Asia, being highly vulnerable to climate change, tends to prioritize environmental issues. Countries like India and China are focusing on renewable energy solutions, while island nations are pushing for global climate action to mitigate the impacts of rising sea levels.
6. Conclusion: The Asian Perspective on Global Affairs
The worldview of Asians is shaped by a combination of historical context, economic forces, political dynamics, and cultural values. As Asia continues to rise as a global economic and political powerhouse, its unique perspectives will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of global relations. Whether it’s through trade, environmental policy, or geopolitical alliances, understanding how Asians see the world is essential for fostering a more interconnected and harmonious global community.
For more information on Asia’s growing influence, check out this article on Asia’s geopolitical impact.

Comment (0)